https://leetcode.com/problems/minimize-the-total-price-of-the-trips/
基本上這題分爲兩個步驟,
- 找出經過所有節點的次數
- 在樹上跑過一次 dp,看減半過後的最佳解
我們先看第一個步驟要怎麼做。
先把 edges 變成 adjacency list g。接下來對於 trips[i],可以從 trips[i][0] 跑過 dfs 或是 bfs 直到經過 trips[i][1]。
用 freq 來記錄經過各個節點的次數, parent 來記錄 「以 trips[i][0] 爲 root,各個節點的 parent 是誰」。
當經過 trips[i][1] 時可以跳出 queue,並且從 trips[i][1] 開始,往上走,邊走邊更新 freq 直到我們抵達 root。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto e: edges){
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
vector<int> freq(n, 0);
for (auto trip: trips){
int start = trip[0];
int end = trip[1];
queue<int> q;
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
vector<int> parent(n, -1);
q.push(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (not q.empty()){
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if (cur == end){
break;
}
for (int next: g[cur]){
if (not visited[next]){
q.push(next);
parent[next] = cur;
visited[next] = true;
}
}
}
for (int i = end; i >= 0; i = parent[i]){
freq[i]++;
}
}
|
或是用 recursion 的方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| for (auto trip: trips){
int start = trip[0];
int end = trip[1];
function<bool(int, int)> dfs = [&](int cur, int p){
if (cur == end){
freq[cur]++;
return true;
}
for (int next: g[cur]){
if (next != p && dfs(next, cur)){
freq[cur]++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
dfs(start, -1);
}
|
dfs(n, p) 會回傳 true 如果以 n 爲 root 的 subtree 包含了 end 這個節點。
可以看著這個圖想想看。
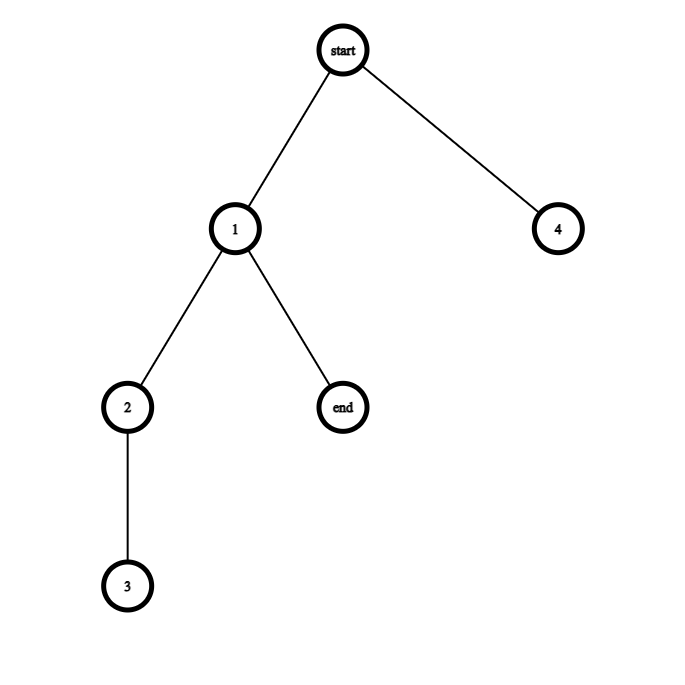
接下來第二個步驟就是在樹上 dp。
定義 dp(i) 爲「0 爲 root 時,以 i 爲 root 的 subtree 在選擇減半與不減半的 minimal cost」。
dp(i)[0] 是減半的 minimal cost,dp(i)[1] 是不減半的 minimal cost。
看起來有點饒口,可以搭配下面這張圖。
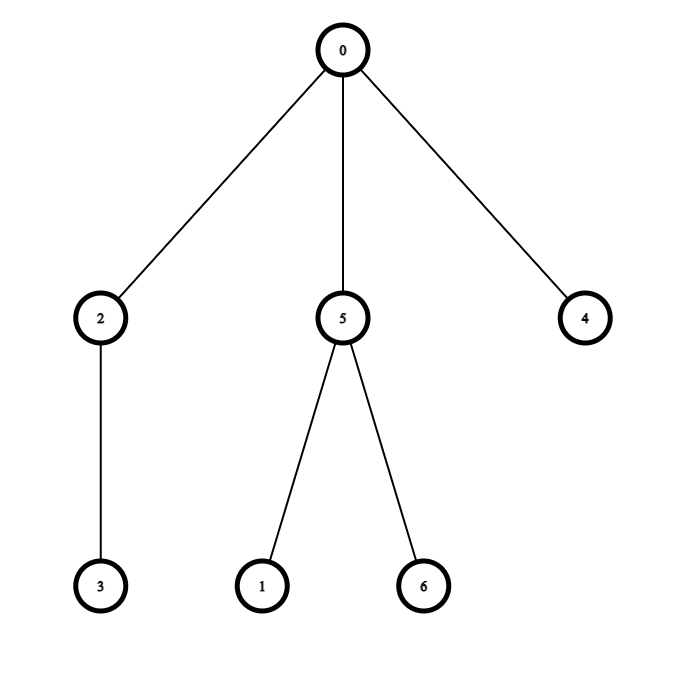
dp(5) 的意思就是 「5 爲 root 的 subtree (也就是 5, 1, 6 這個樹)在選擇減半與不減半(price[5] 減半與不減半)的 minimal cost」
對於 dp(i),如果選擇減半的話,i 這個節點的 cost 是 freq[i] * price[i] / 2,但是代價是 i 的 children 都不能減半。
不選擇減半的話,i 這個節點的 cost 是 freq[i] * price[i],但是 i 的 children 可以選擇減半(可以減半,但是不一定要)。
所以對於 i,不減半的最佳選擇就是 freq[i] * price[i] + sum(min(dp(j)[0], dp(j)[1])),j 是 i 的 children。
減半的最佳選擇就是 freq[i] * price[i] / 2 + sum((dp(j)[1]),j 是 i 的 children。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| function<pair<int, int>(int, int)> dp = [&](int cur, int prev) -> pair<int, int>{
int no_half = freq[cur] * price[cur];
int half = no_half / 2;
for (int next: g[cur]){
if (next == prev){
continue;
}
auto [half_next, no_half_next] = dp(next, cur);
no_half += min(half_next, no_half_next);
half += no_half_next;
}
return {half, no_half};
};
auto ans = dp(0, -1);
return min(ans.first, ans.second);
|

